- Home
- Contact Us
- News & Events
- Awards
- AAEES Awards Criteria
- 40 Under 40 Recognition Program
- Edward J.Cleary Award
- Excellence in Environmental Engineering and Science Education
- Gordon Maskew Fair Award
- Honorary Member
- International Honorary Member
- Ralph and Joe Bales Graber Science Award
- Stanley E. Kappe Award
- Environmental Communications Awards Competition
- Excellence in Environmental Engineering and Science Competition
- The AAEES Chapter Blue Marble Award
- Resources
- AAEES Microcredentials
- Annual Reports
- AAEES Press Releases
- AAEES Website How To VIdeos
- Environmental Engineer and Scientist
- Environmental Engineering Body of Knowledge
- PFAS Resources
- Specialty Examination Guide
- Students and Young Professionals Resources
- Who's Who in Environmental Engineering & Science®
- Leadership Opportunities
- Membership
- Donate
- Jobs
2022 Excellence in Environmental Engineering and Science® Awards Competition Winner
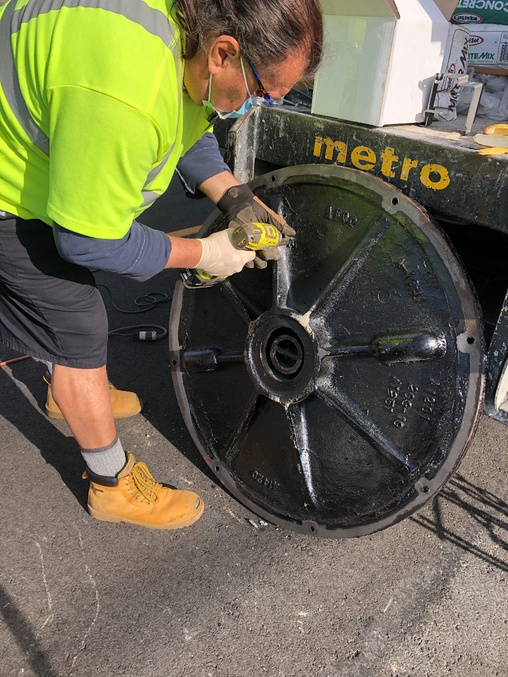
Honor Award - Operations/ManagementOptimized Odor Control and Cleaning in Sewer SystemEntrant: Orange County Sanitation District Entrant Profile 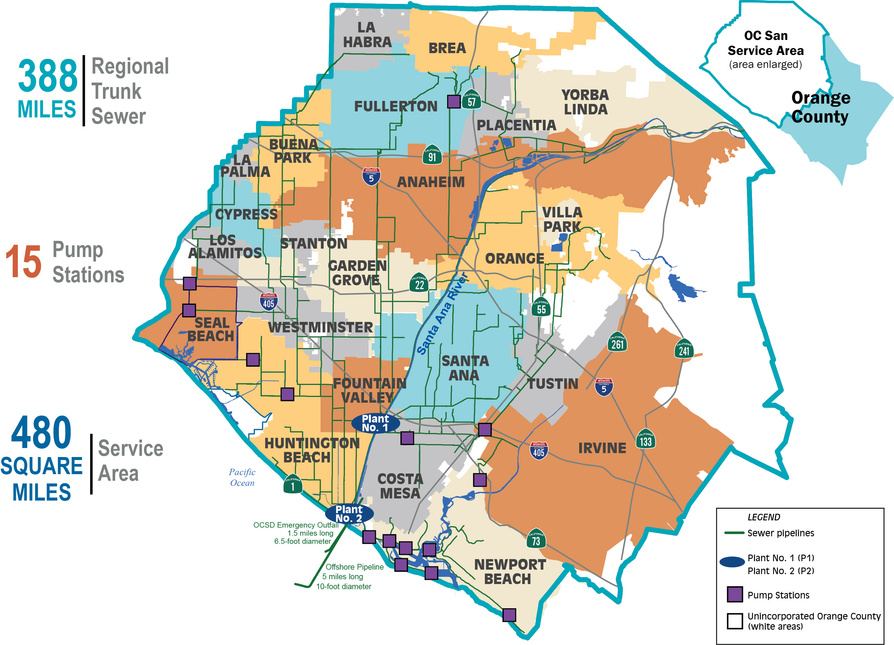
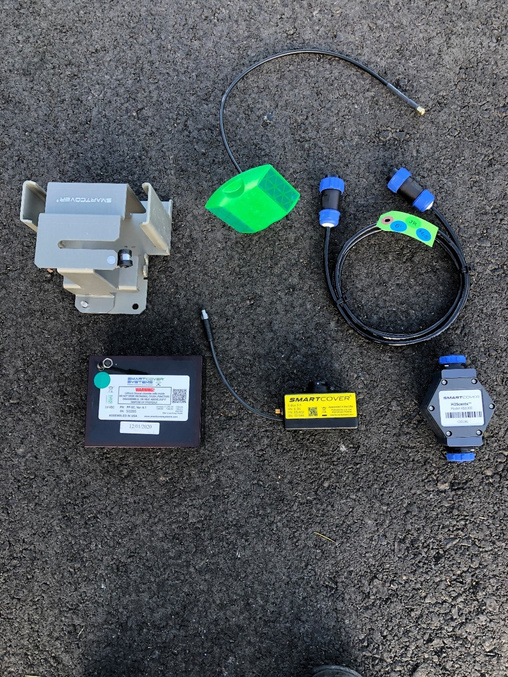
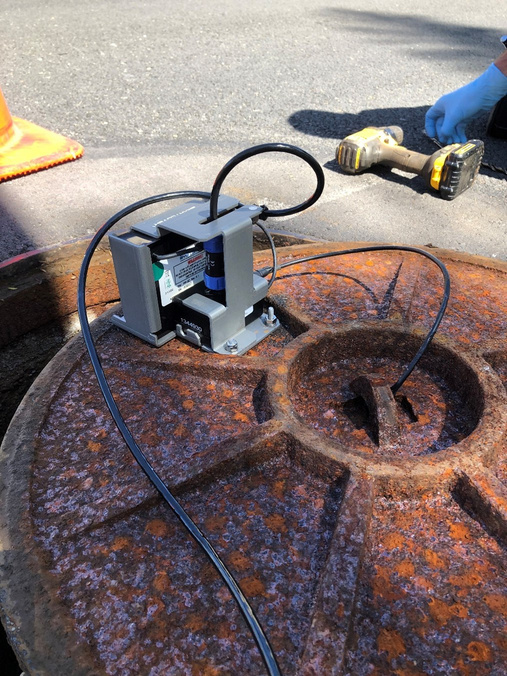
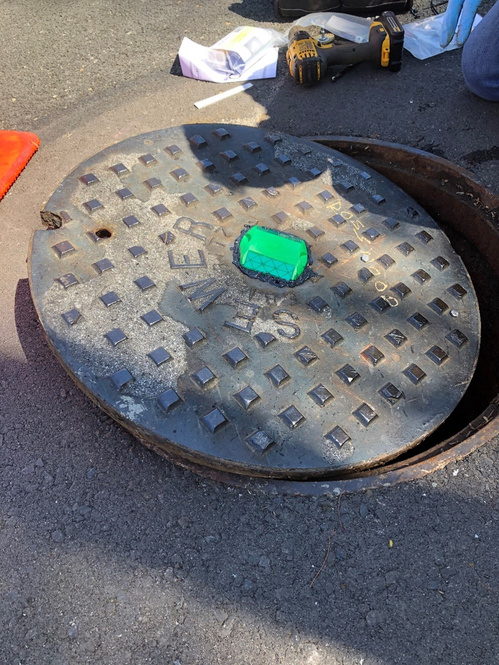
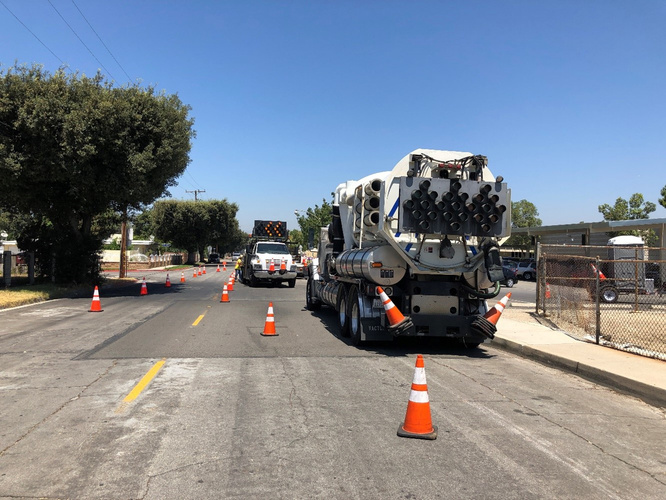
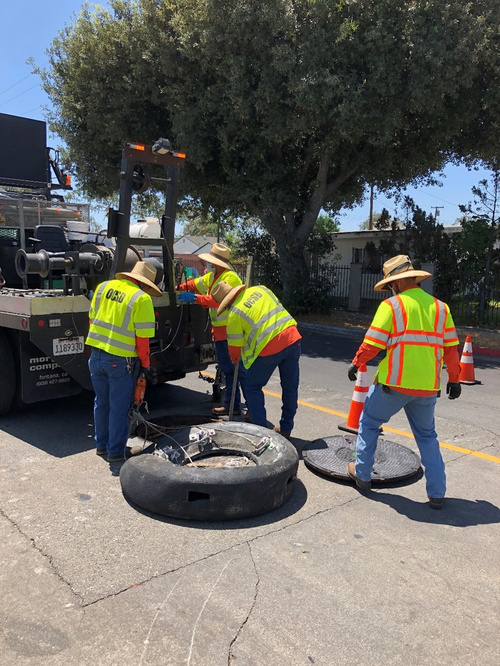
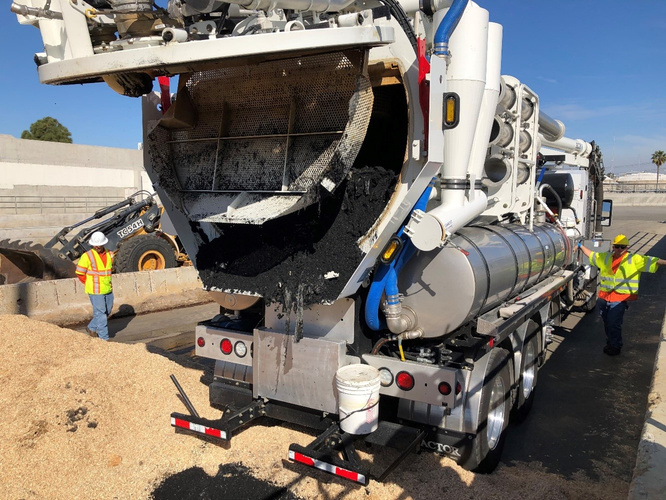
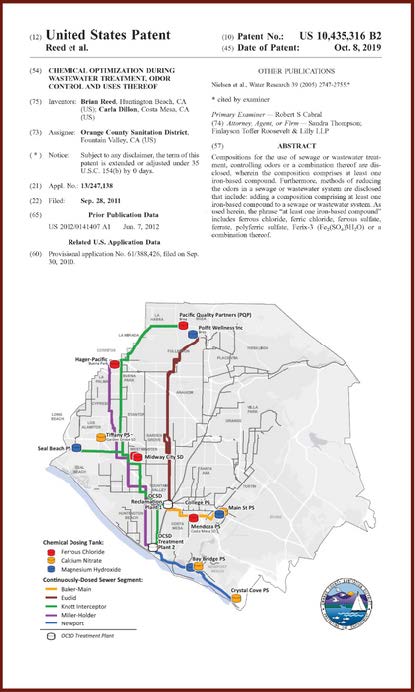
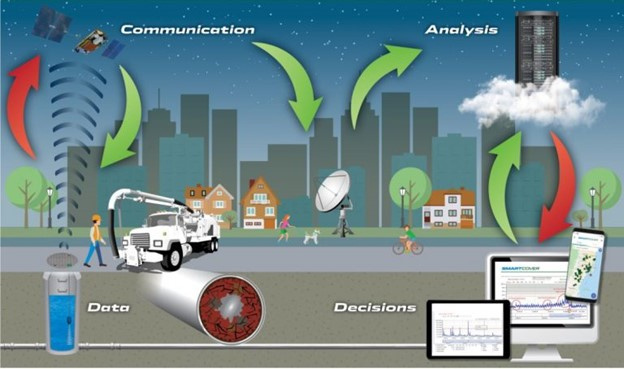
The Orange County Sanitation District (OC San) is a special district governed by a 25-member Board of Directors comprised of 20 cities, four special districts, and one representative from the Orange County Board of Supervisors. OC San provides wastewater collection, treatment, and recycling for approximately 2.6 million people living within a 480-square-mile area of central and northwestern Orange County, California (CA). Our facilities include 388 miles of sewer pipes, located throughout the county. Together both plants currently treat around 180 million gallons per day (mgd) that is sent to our two treatment plants: Plant No. 1 in Fountain Valley and Plant No. 2 in Huntington Beach, CA. Located in the second most densely populated county in the state, OC San has operated since 1954. With the population volume and density exhibited in Orange County, OC San has looked to technology to better manage its collection system. Resources need to be managed appropriately while striving to operate and maintain our facilities to minimize impacts within our community as they relate to odor, noise, traffic, and environmental risk associated with sewer spills. OC San is tasked with providing services to 2.6 million people and must evolve to ensure cost-effective services to rate payers. To ensure operational resiliency OC San deployed technology in its collection system to have active tools for managing nuisance odors, optimizing cleaning tasks and intervals, and a means to alert of a potential sewer spill looming. Building this “smart” collection system was accomplished with efforts of Collections Operations and Maintenance staff and the SmartCover company. Project DescriptionOverviewThe Orange County Sanitation District (OC San) is responsible for 388 miles of sanitary sewers and 15 offsite pump stations that culminate at two treatment plants. Since the conveyance and treatment of wastewater is a naturally odorous process, OC San has developed an extensive collection system odor-control program. The program combines chemical treatment using a patented process, continuous dosing rate optimization using state-of-the-art SmartCover, and proven mechanical cleaning techniques to minimize fugitive odor emissions throughout extensive service areas. The liquid-phase odor control element maintains average vapor-phase hydrogen sulfide below 45 parts per million, reducing odors and corrosion in the regional trunk system and suppressing odors at the treatment plants. A study was conducted as part of OC San's ongoing efforts to diversify and improve odor control performance within its collection system while minimizing cleaning intervals. The objectives were to identify ways of reducing OC San's exposure to volatile chemical prices and optimize resources utilized to clean sewers. A collection system trunk line known as the Baker- Main Interceptor located in Costa Mesa and is 90-inches in diameter was the subject of this study. It involved adding alkalinity by simultaneously dosing magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) to enhance the performance of calcium nitrate (Ca(NO₃)₂) and ferrous chloride (FeCl₂) while lowering the overall chemical usage. The approach is memorialized in the patent issued in 2019 to OC San. The technology is based on sewage alkalinity's syngergistic effect, improving performance. The test results show that dosing Ca(NO₃)₂) in combination with Mg(OH)₂) while adding (FeCl₂) downstream is a cost-effective way to achieve consistent performance with reduced chemical usage. The optimization efforts OC San implemented have improved the control of odors and corrosion and prevented sewer overflows using a technology approach that combines flow monitoring and various sensors. The continuous remote monitoring of sewers with artificial intelligence (AI) improves collection system visibility. AI prevents sanitary sewer spills while optimizing the sewer cleaning schedules and reliably measures real-time hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) levels over extended periods to minimize fugitive odor emissions and preserve assets throughout an extended service area. Comprehensive and Integrated ApproachAir: Air quality is improved by reducing the release of fugitive odors from wastewater conveyance and treatment. Public odor nuisances are avoided, thus fulfilling a desired level of service. Water: Odor control is achieved without increasing potable water use or negatively impacting water sources or watersheds. Odor control supports the overall process of wastewater treatment, which is necessary to protect receiving waters and promote water reclamation and reuse. This synergistic approach provides an avenue for meeting this needs without creating a public nuisance. Land: Inorganic components of odor treatment chemicals (such as iron) add to the solids loading of a treatment plant and ultimately to the residual solids that are land applied or landfilled. Reduced chemical usage reduces the land impacts of wastewater treatment. 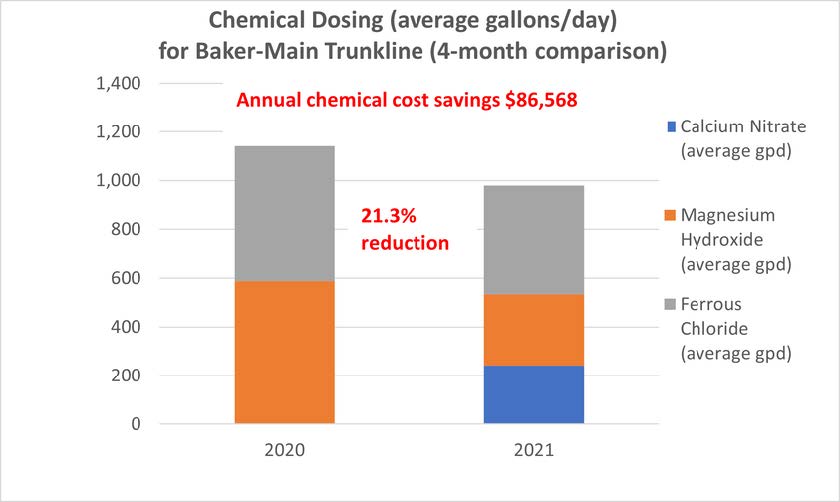 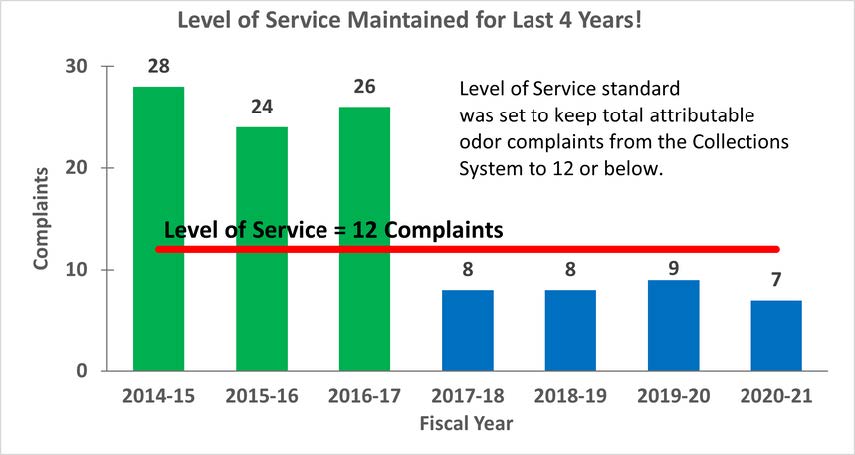
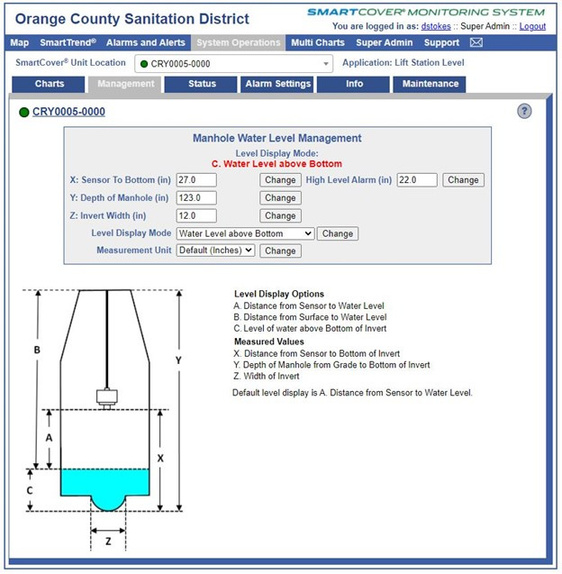
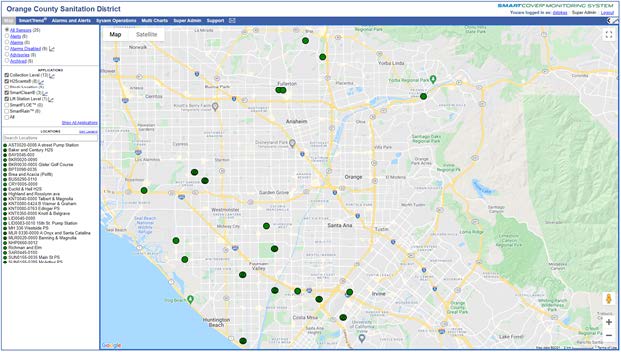
QualityThe effectiveness and quality of the odor control program are shown by the dramatic decrease in odor complaints received during the past two years while also reducing chemical costs. Annual chemical cost savings in the Baker-Main Interceptor of $86,568 (a 10.4% reduction) and 18% H₂S reduction with the OC San technology approach are projected from data obtained during a four-month field treatment comparison with and without calcium nitrate in combination with magnesium hydroxide and ferrous chloride. Using all three chemicals together saves money (Figure 1) and controls H₂S more effectively while lowering chemical consumption overall. Projecting Baker-Main trunk results for two additional trunk lines that use the same chemicals and applying the same savings of 10.4% would result in an annual savings $95,685 for OC San's Knott trunk line and $24,469 for Newport trunk line. OC San's stated goal is to have no more than 12 complaints annually from its 480-squaremile service area (Figure 2). Collection odor complaint goals have been met for the last four years. Originality and InnovationOC San has coupled its patented approach to wastewater collection system odor control with field technology from SmartCover Systems. The data from the field technology has provided an avenue to optimize chemical dosing rates for cost savings and reduce system cleaning frequency. Cost savings are realized from reduced chemical usage and unnecessary sewer cleaning. Leaning on the algorithm from SmartCover aids in operational optimization through its real-time monitoring of of H₂S levels and wastewater flow conditions at critical locations. ComplexityOC San's 388-mile collection system serves residential, commercial, and industrial customers. The wastewater characteristics and flow profile in any given trunk line are impacted by water conservation measures, periodic drought conditions, changes in industrial dischargers in the service area, and flow diversions for the Groundwater Replenishment System's indirect potable reuse. In addition, OC San receives desalter concentrate and industrial and domestic wastewater from the upper Santa Ana River Basin. These factors combine to make odor control and cleaning requirements throughout the system site-specific and dynamic. Velocity changes in the pipelines pose challenges for determining the appropriate interval for cleaning the pipe, so transitioning from a calendar-based approach to a condition-based was made possible by the field technology of SmartCover Systems. Social and Economic AdvancementThere is general public intolerance of odors associated with wastewater treatment operations. This is codified in the local air quality ' 'regulator's nuisance prohibition ["A person shall not discharge from any source whatsoever…air contaminants…which cause injury, detriment, nuisance, or annoyance…to the public…" (SCAQMD Rule 402)]. Additionally, sewer cleaning crews on the streets cause traffic constraints on the public right-of-way. Social Advancement: OC San's odor mitigation program has dramatically decreased odor nuisances in one of California's most densely populated areas, allowing residents to enjoy the region's natural resources and improve their quality of life. The secondary benefit is that a reduced carbon footprint arises from an optimized sewer cleaning schedule that reduces operational equipment hours while minimizing the traffic impacts from these vehicles on the road. Economic Advancement: An efficient and optimized program provides effective odor control while decreasing operational costs, a return to our ratepayers. Click images to enlarge in separate window. Click here to return to the list of 2022 winners. |